Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 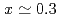
伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 幸田 章宏*; 中村 惇平*; 下村 浩一郎*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
We report on muon spin relaxation ( SR) measurements in a mixed perovskite compound, (LaAlO
SR) measurements in a mixed perovskite compound, (LaAlO )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 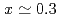 (LSAT), which is widely used as a single-crystalline substrate for thin film deposition. In zero applied field (ZF), muon depolarization due to the distribution of nuclear dipole fields was observed in the temperature range from 4 K to 270 K. Interestingly,
(LSAT), which is widely used as a single-crystalline substrate for thin film deposition. In zero applied field (ZF), muon depolarization due to the distribution of nuclear dipole fields was observed in the temperature range from 4 K to 270 K. Interestingly,  SR time spectra in ZF maintained a Gaussian-like feature over the entire range, while the depolarization rate exhibited a monotonic decrease with increasing temperature. This behavior may be attributed to the thermally activated diffusion of muons between a few adjacent sites within a confined space of the angstrom scale, where the motionally averaged local field that each muon experiences can remain non-zero and result in maintaining the Gaussian-like line shape. The spatial distribution of electrostatic potential at lattice interstices evaluated via density functional theory calculations suggests that such a restriction of muon diffusion paths can be caused by the random distribution of cations with different nominal valences in the mixed perovskite lattice.
SR time spectra in ZF maintained a Gaussian-like feature over the entire range, while the depolarization rate exhibited a monotonic decrease with increasing temperature. This behavior may be attributed to the thermally activated diffusion of muons between a few adjacent sites within a confined space of the angstrom scale, where the motionally averaged local field that each muon experiences can remain non-zero and result in maintaining the Gaussian-like line shape. The spatial distribution of electrostatic potential at lattice interstices evaluated via density functional theory calculations suggests that such a restriction of muon diffusion paths can be caused by the random distribution of cations with different nominal valences in the mixed perovskite lattice.
葛下 かおり; 森本 正太郎*; 那須 三郎*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 329-333(1-4), p.736 - 737, 2003/05
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:45.98(Physics, Condensed Matter)ぺロブスカイト型鉄酸化物の物理的性質はFeO 八面体のネットワークに関係している。SrFeO
八面体のネットワークに関係している。SrFeO では起こらない電荷分離(2Fe
では起こらない電荷分離(2Fe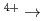 Fe
Fe + Fe
+ Fe )が、SrのLaへの置換や次元性の変化によるFeO
)が、SrのLaへの置換や次元性の変化によるFeO 八面体のネットワークの切断により発現する。また、Sr
八面体のネットワークの切断により発現する。また、Sr Fe
Fe O
O のFeを40%Coに置換すると、磁性は反強磁性から強磁性へと変化し電荷分離も抑制される。
のFeを40%Coに置換すると、磁性は反強磁性から強磁性へと変化し電荷分離も抑制される。
 ; Electronic structure of the hydrogen-like defects and their potential use in depth-resolved detection of oxygen vacancies
; Electronic structure of the hydrogen-like defects and their potential use in depth-resolved detection of oxygen vacancies伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 幸田 章宏*; 下村 浩一郎*
no journal, ,
Recent  SR studies in SrTiO
SR studies in SrTiO focusing on the following two aspects will be presented. (i) Electronic structure of interstitial Mu in SrTiO
focusing on the following two aspects will be presented. (i) Electronic structure of interstitial Mu in SrTiO : The formation of a Mu
: The formation of a Mu -Ti
-Ti polaron complex was observed upon implantation of positive muons into stoichiometric SrTiO
polaron complex was observed upon implantation of positive muons into stoichiometric SrTiO . The small activation energy of 30(3) meV found for the thermal dissociation of the Mu
. The small activation energy of 30(3) meV found for the thermal dissociation of the Mu -Ti
-Ti polaron complex suggests that the strain energy required to distort the lattice is comparable to the electronic energy gained by localizing the electron. (ii) Potential use of
polaron complex suggests that the strain energy required to distort the lattice is comparable to the electronic energy gained by localizing the electron. (ii) Potential use of  SR for oxygen vacancy detection in SrTiO
SR for oxygen vacancy detection in SrTiO : The oxygen vacancy (V
: The oxygen vacancy (V ) is a major defect species in perovskite titanates, having a strong impact on their electrical, optical, and dielectric properties. In spite of the importance of the defect, experimental techniques that can directly detect V
) is a major defect species in perovskite titanates, having a strong impact on their electrical, optical, and dielectric properties. In spite of the importance of the defect, experimental techniques that can directly detect V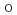 are still limited. Through a series of
are still limited. Through a series of  SR measurements on oxygen-deficient SrTiO
SR measurements on oxygen-deficient SrTiO we revealed that there is a clear positive correlation between the muon spin relaxation rate and the carrier concentration, which is expected to be roughly proportional to the V
we revealed that there is a clear positive correlation between the muon spin relaxation rate and the carrier concentration, which is expected to be roughly proportional to the V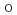 concentration. This, together with the variability of muon implantation depth, suggests that the
concentration. This, together with the variability of muon implantation depth, suggests that the  SR spectroscopy is potentially suitable for the depth-resolved analysis of V
SR spectroscopy is potentially suitable for the depth-resolved analysis of V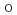 distribution in perovskite oxides, which is complementary to cation vacancy-sensitive techniques, such as positron annihilation spectroscopy.
distribution in perovskite oxides, which is complementary to cation vacancy-sensitive techniques, such as positron annihilation spectroscopy.
 SR as a potential tool for depth-resolved detection of oxygen vacancies in perovskite oxides
SR as a potential tool for depth-resolved detection of oxygen vacancies in perovskite oxides伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 幸田 章宏*; 下村 浩一郎*
no journal, ,
Oxygen vacancy (V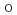 ) is a major defect species in perovskite oxides, having a strong impact on their electrical, optical, and dielectric properties. In spite of its importance, experimental techniques that can directly detect V
) is a major defect species in perovskite oxides, having a strong impact on their electrical, optical, and dielectric properties. In spite of its importance, experimental techniques that can directly detect V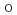 are still limited. Through a series of
are still limited. Through a series of  SR measurements on oxygen-deficient SrTiO
SR measurements on oxygen-deficient SrTiO , we revealed that there is a clear positive correlation between the muon spin relaxation rate and the carrier concentration, which is expected to be roughly proportional to the V
, we revealed that there is a clear positive correlation between the muon spin relaxation rate and the carrier concentration, which is expected to be roughly proportional to the V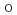 donor concentration. This, together with the variability of muon implantation depth, suggests that
donor concentration. This, together with the variability of muon implantation depth, suggests that  SR spectroscopy is potentially suitable for depth-resolved analysis of V
SR spectroscopy is potentially suitable for depth-resolved analysis of V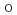 distribution in perovskite oxides, which is complementary to cation vacancy-sensitive techniques, such as positron annihilation spectroscopy.
distribution in perovskite oxides, which is complementary to cation vacancy-sensitive techniques, such as positron annihilation spectroscopy.